WHAT IS POSTMODERN ARCHITECTURAL STYLE?
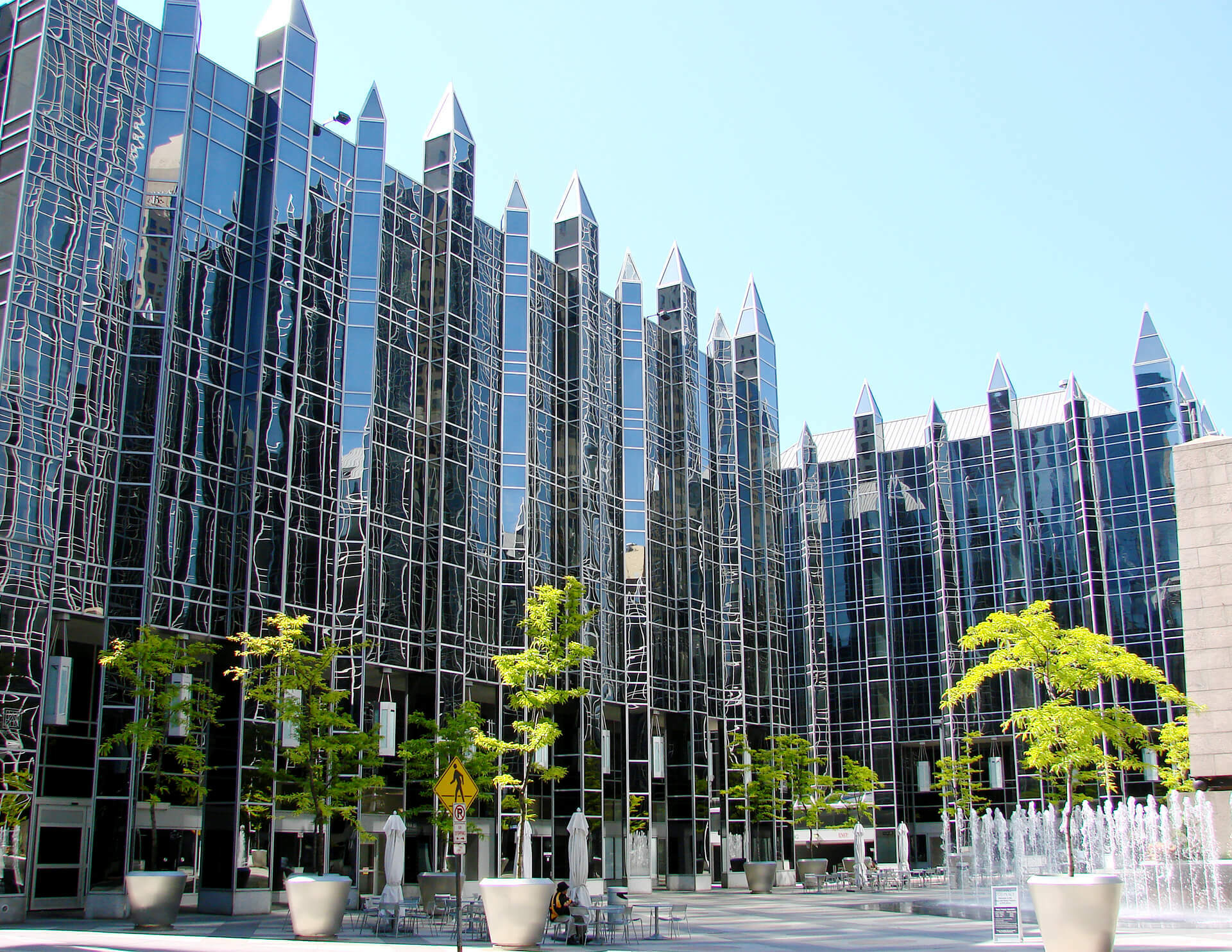
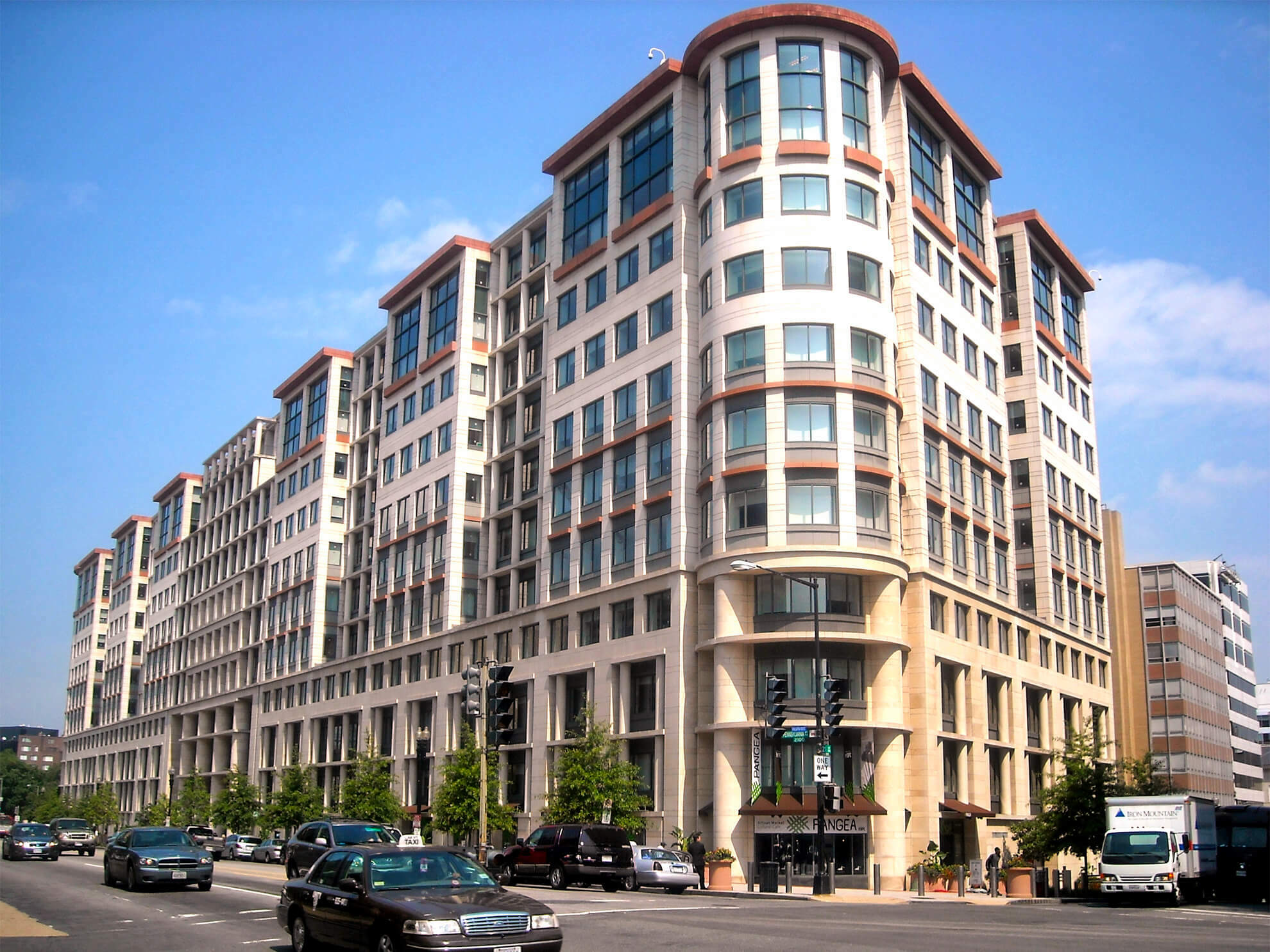
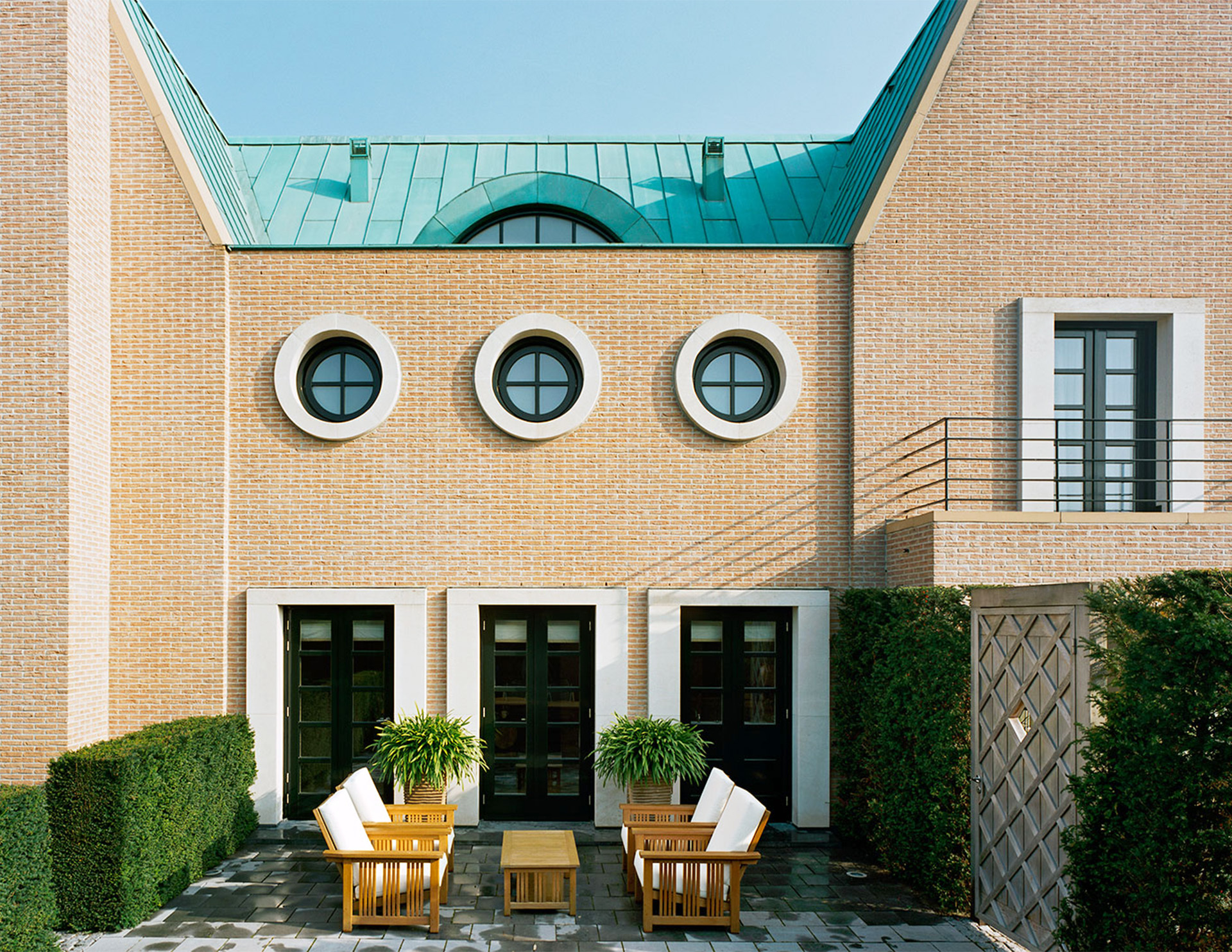
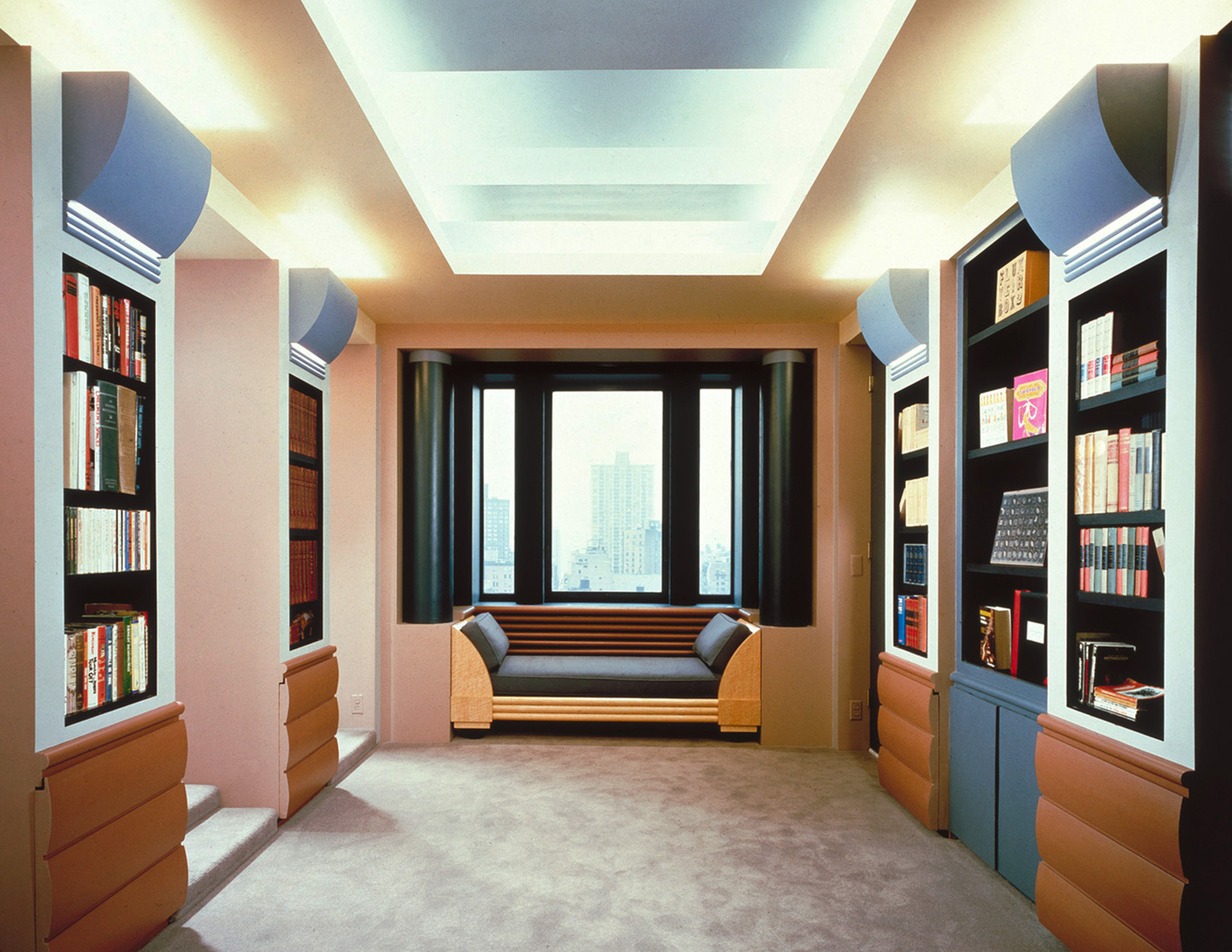
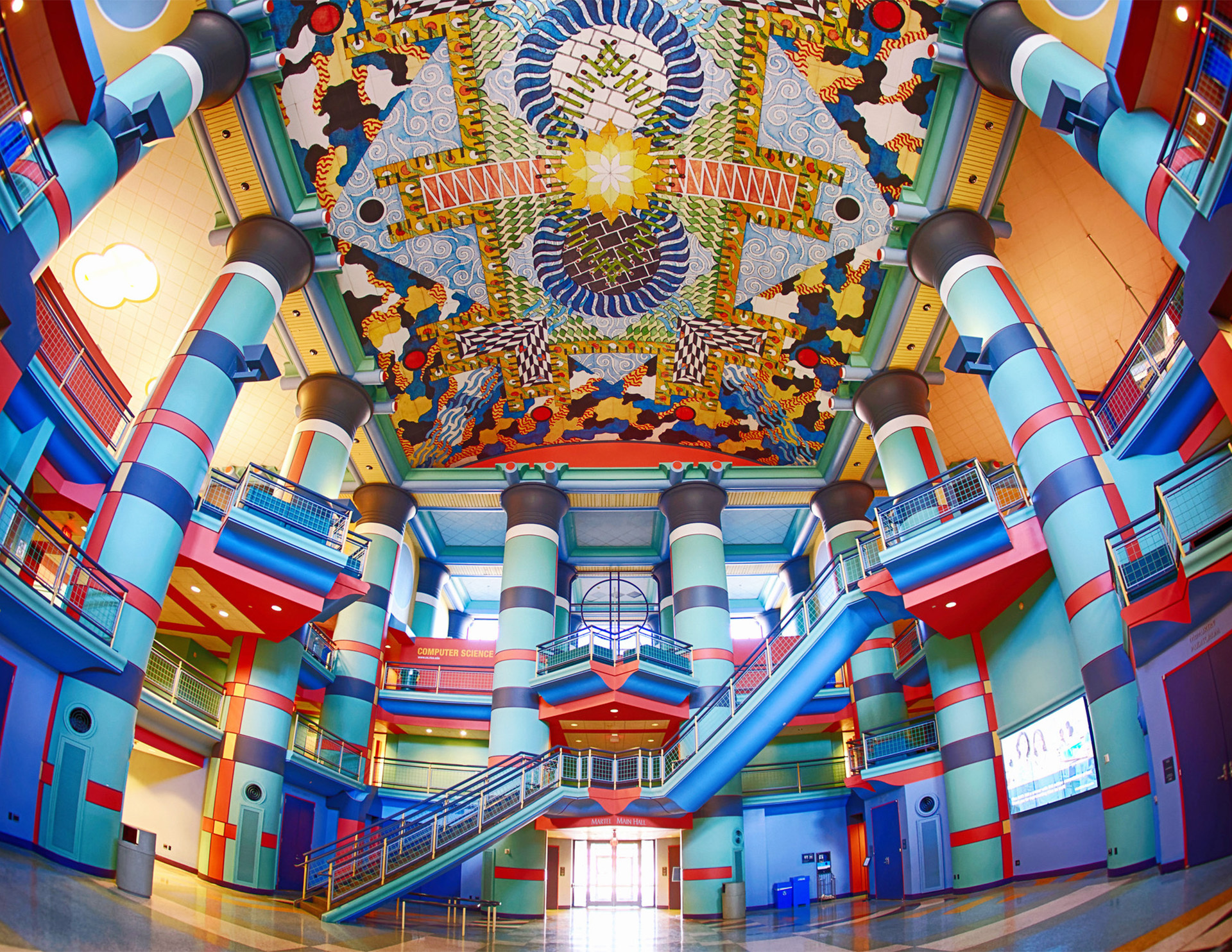
The Postmodern style is a response to modern architecture. Postmodernism departs from modernism in opposition to the modernists’ rigid ideals that dictate simplicity, abstraction, and simple shapes. Unlike modernism, Postmodernism encouraged creativity in asymmetry, fragmentation, complexity, humor, color, playfulness, classical motifs, and various materials and shapes.
Modernism rejects any historical reverence and celebrates the future as a cosmopolitan, eclectic mishmash involving all artistic eras and trends.
See examples of Postmodern architecture & mouldings.
CHARACTERISTICS OF POSTMODERN ARCHITECTURE
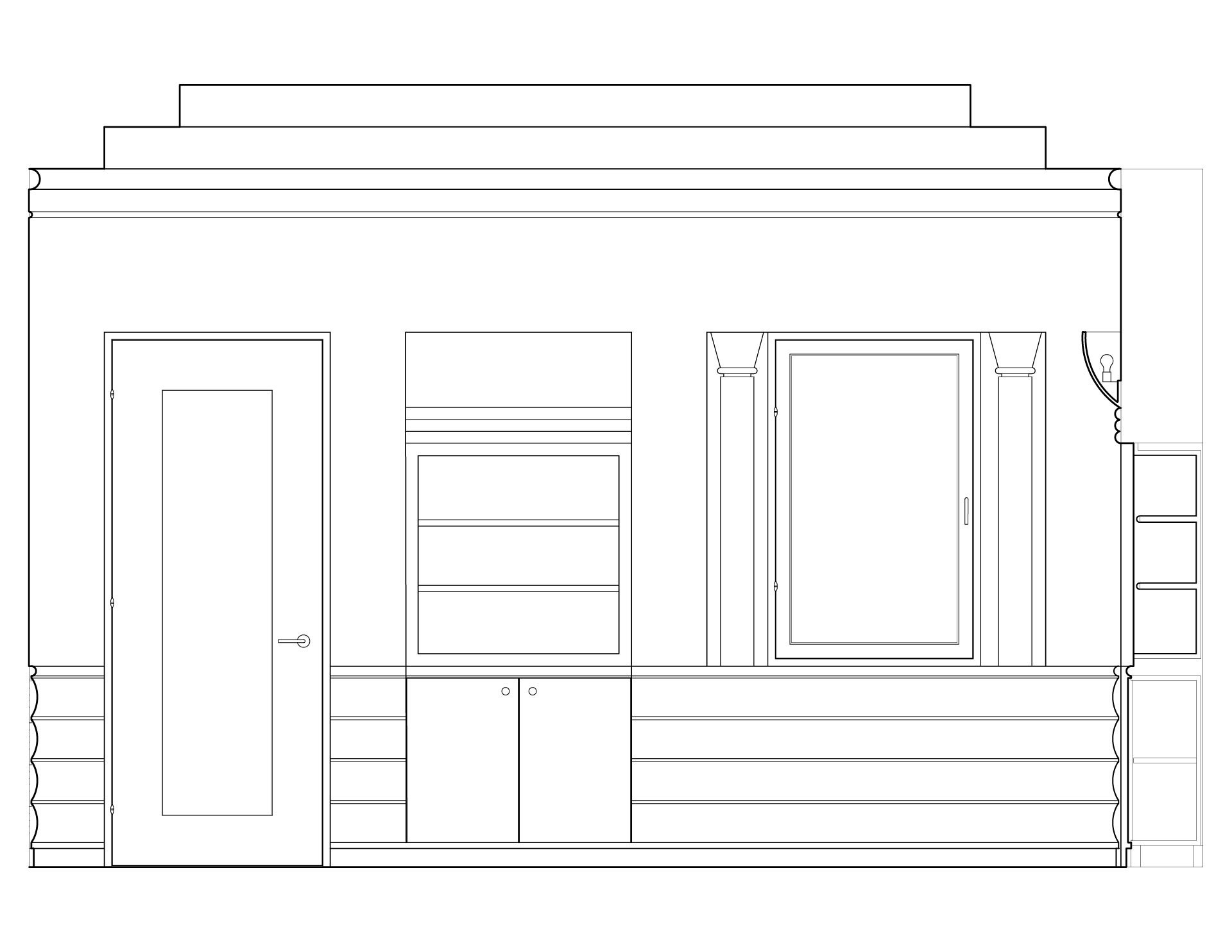
Historic Postmodern style homes went against traditional, classical styles by embracing experimentation with an “anything goes” attitude. They feature combinations of traditional styles such as Neoclassical, Arts and Crafts,and Art Deco, but have much more distinguishable features.
Common elements of Postmodern style:
- Eclectic, playful, and colorful designs
- Usually asymmetric
- Oversized shapes
- Curved forms
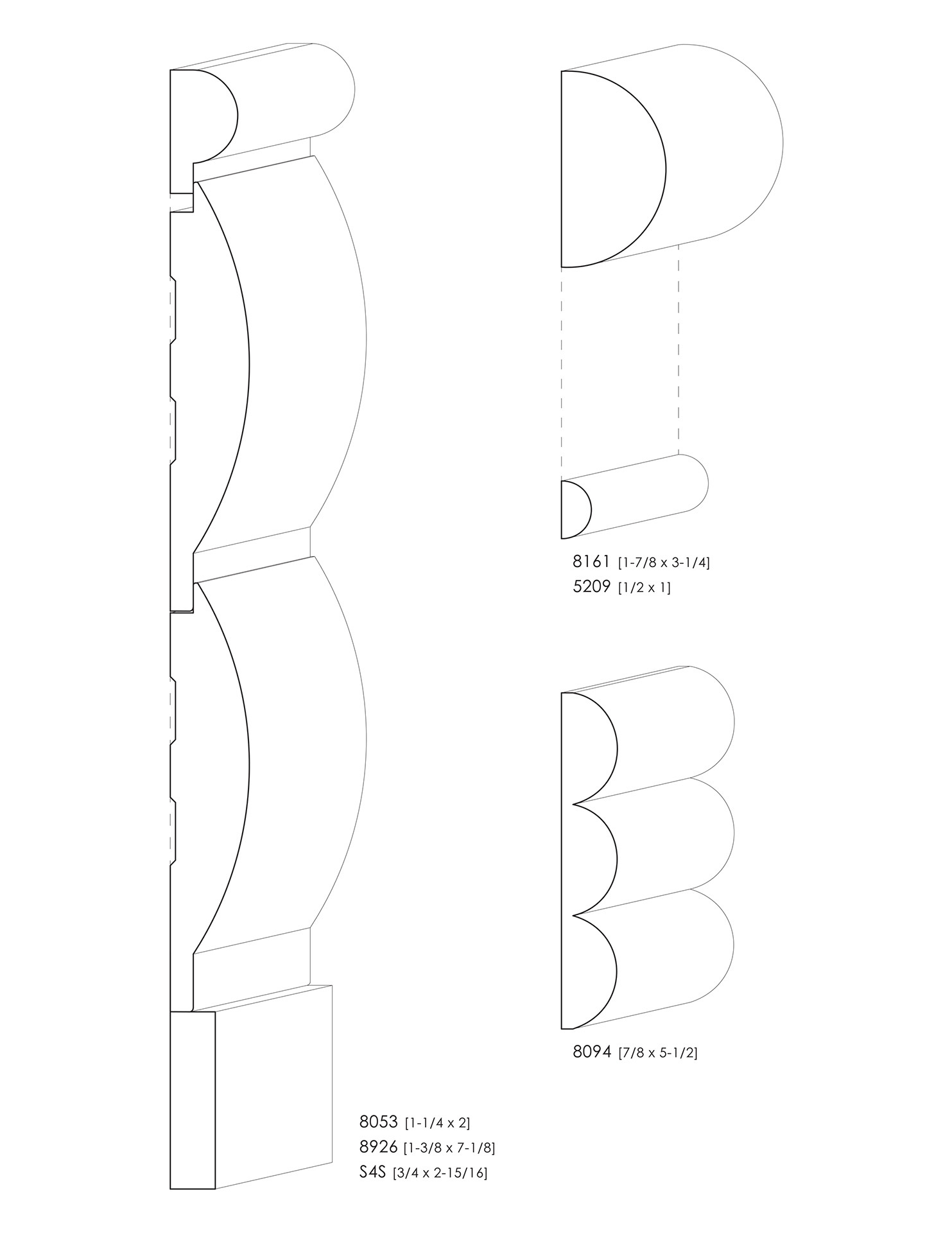
POSTMODERN STYLE MOULDINGS
Postmodernist mouldings can include any of the traditional shapes, but they tend to be limited to usually oversized, basic shapes.
Rather than mitering corners, Postmodernist usage often cuts the moulding profiles off perpendicular, allowing the profile to be seen on edge. The half-round moulding is especially common in Postmodern designs.
HISTORY OF POSTMODERN ARCHITECTURE
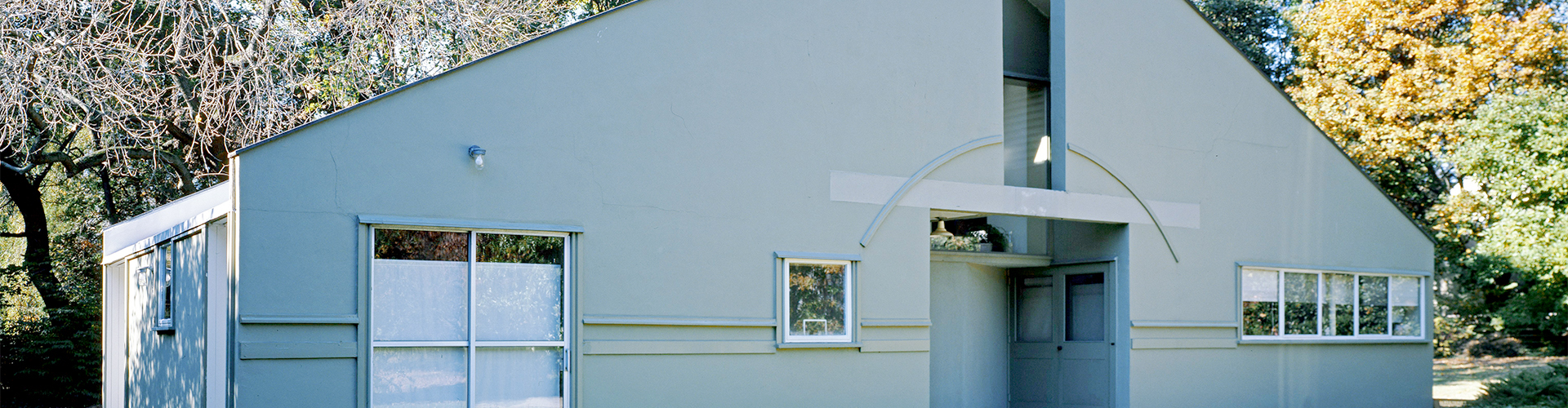
Architect Robert Venturi is the founding father of Postmodernism. He originated the theory captured in his book, Complexity and Contradiction in Architecture (1966), that “less is a bore.” Postmodern architecture started as a critique against traditional styles of architecture.
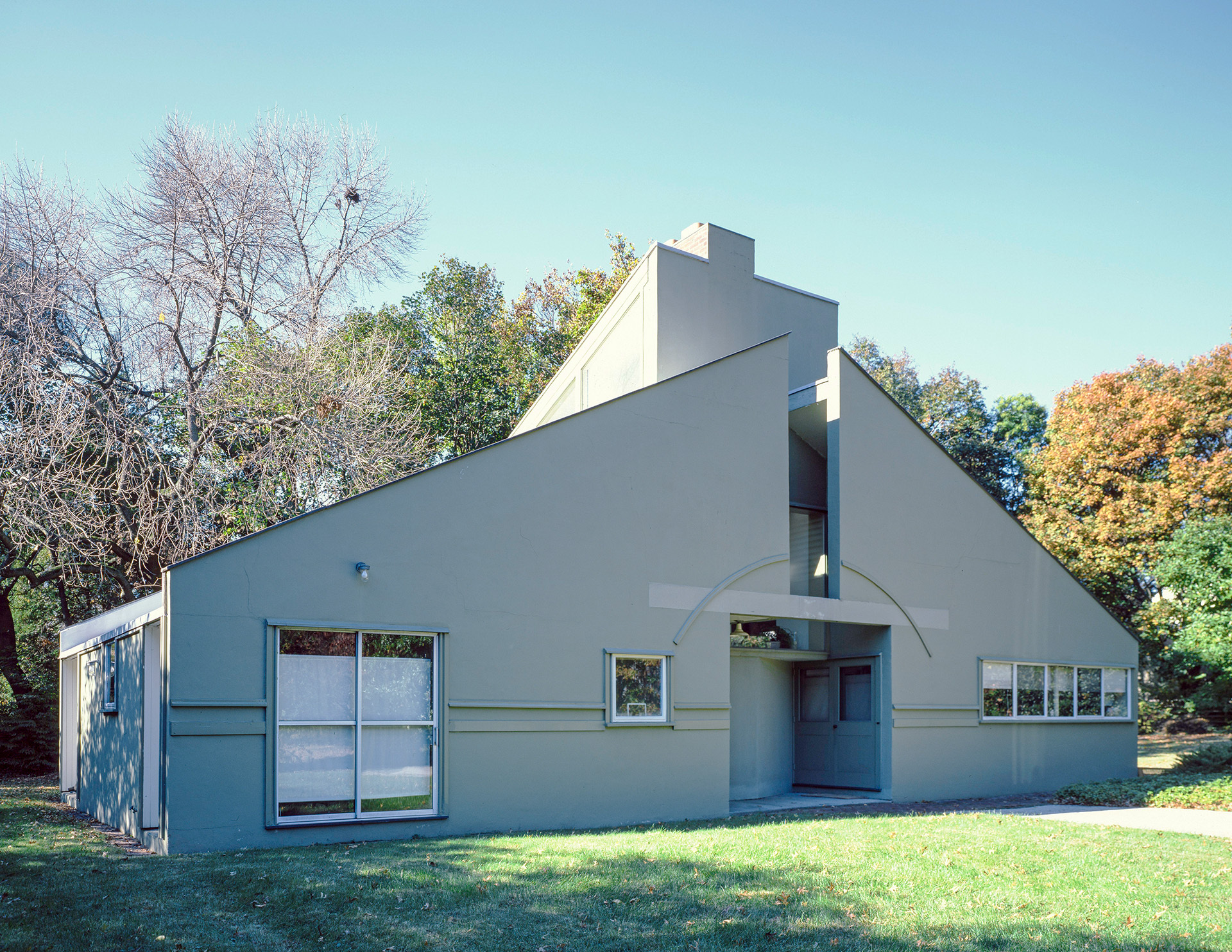
One of the earliest examples of postmodern architecture is the Vanna Venturi House, which was built by Venturi and completed in 1964. Venturi had an eye for dynamic pizzazz. He notes that Postmodern is a “gentle manifesto for a non-straightforward architecture” without any limitations to inclusion without exclusion.