WHAT IS ART MODERNE ARCHITECTURAL STYLE?
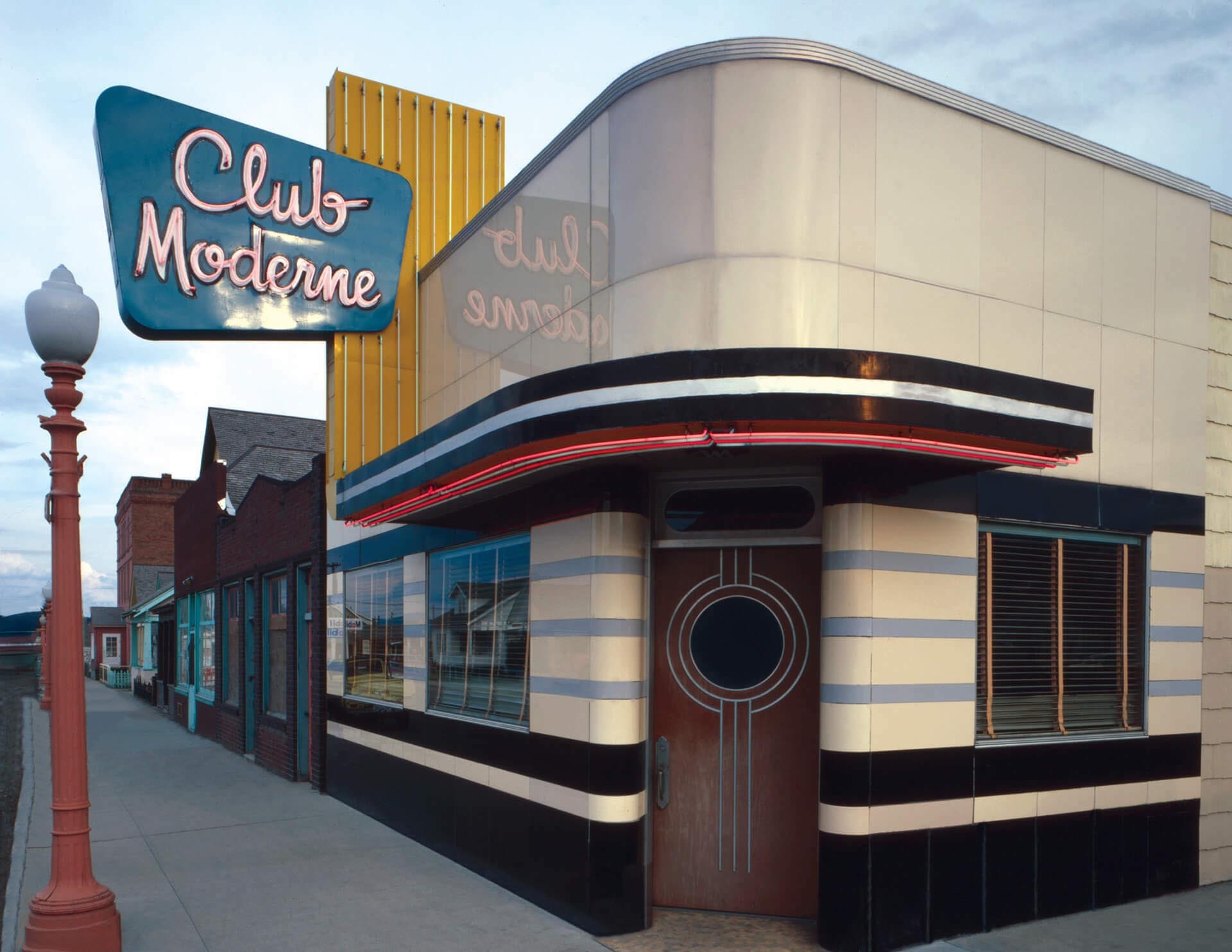
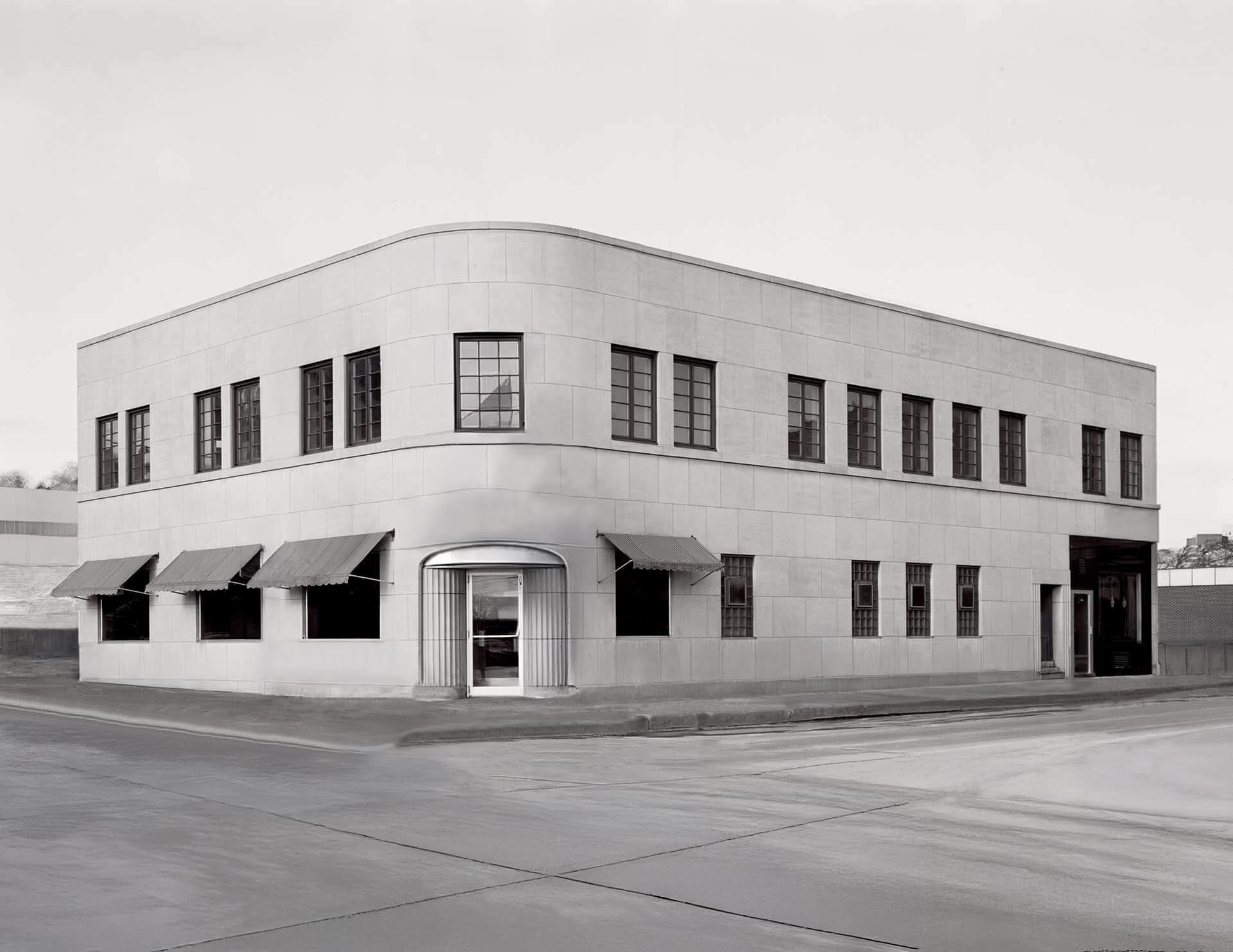
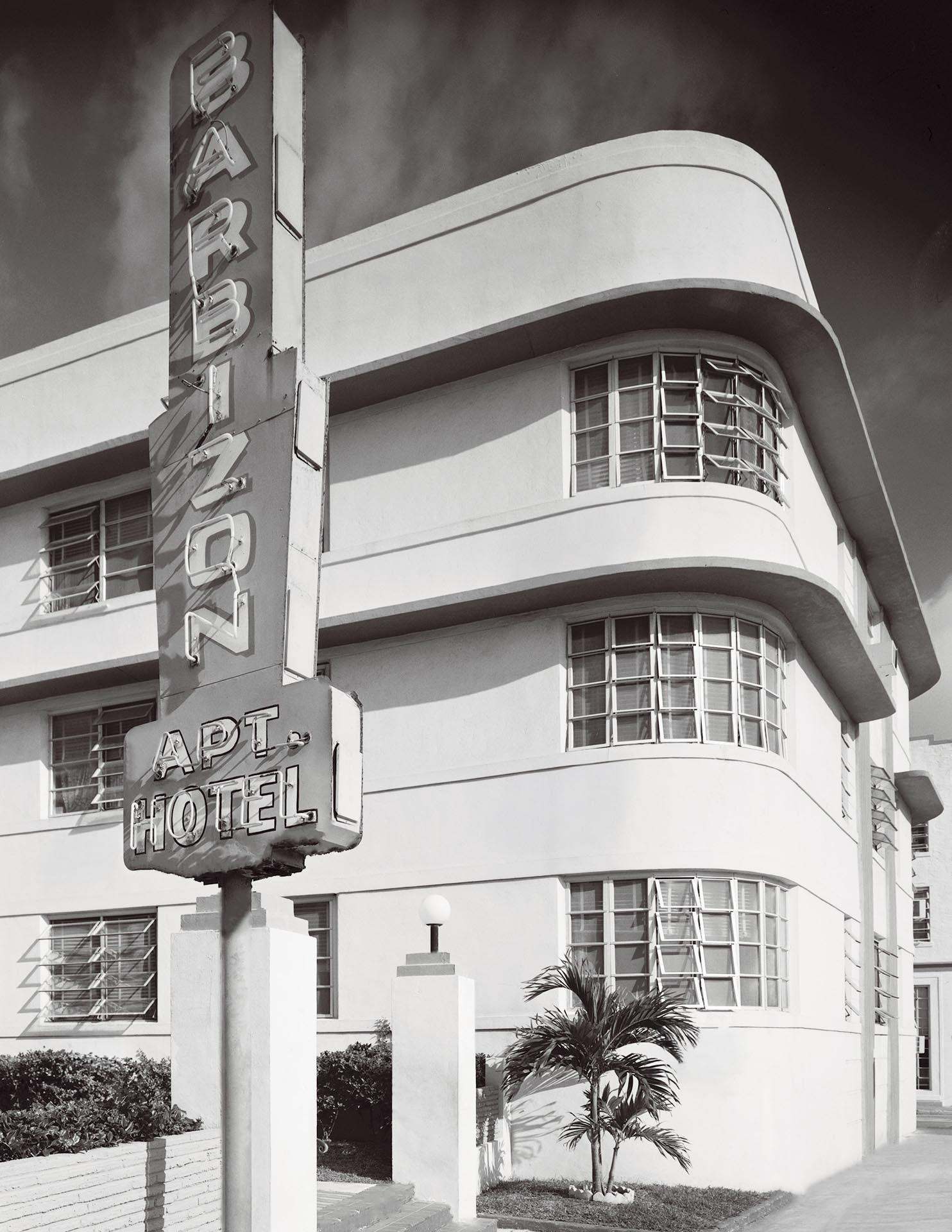
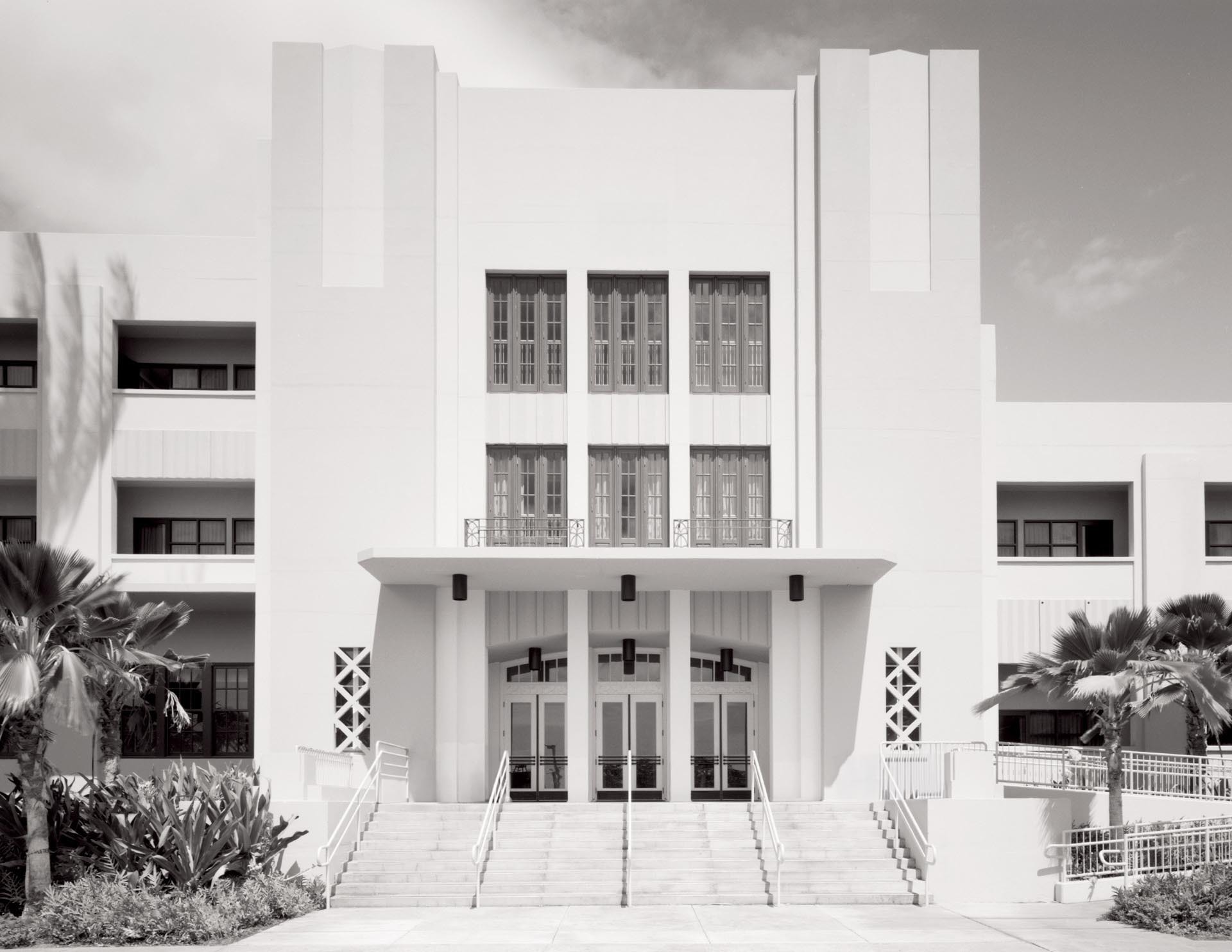
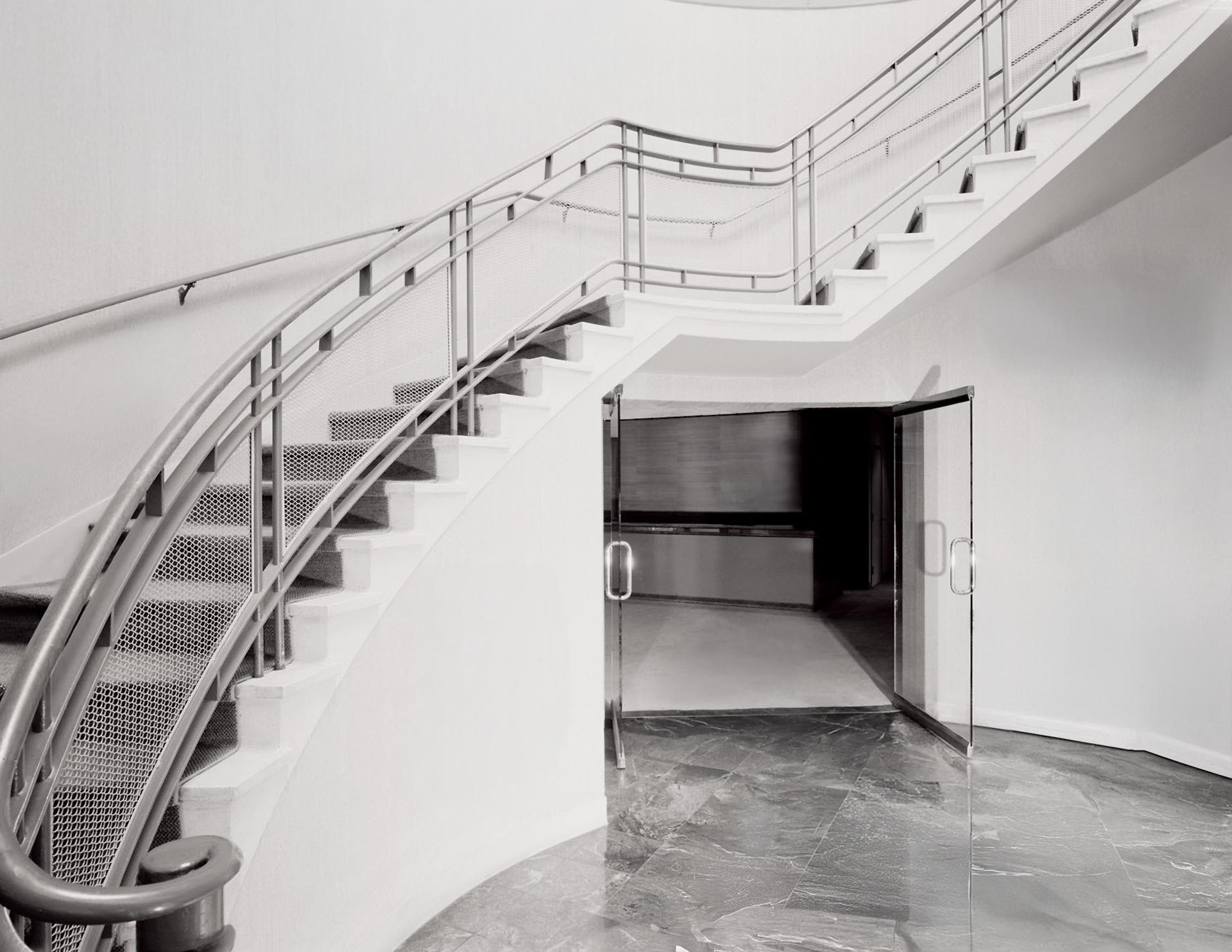
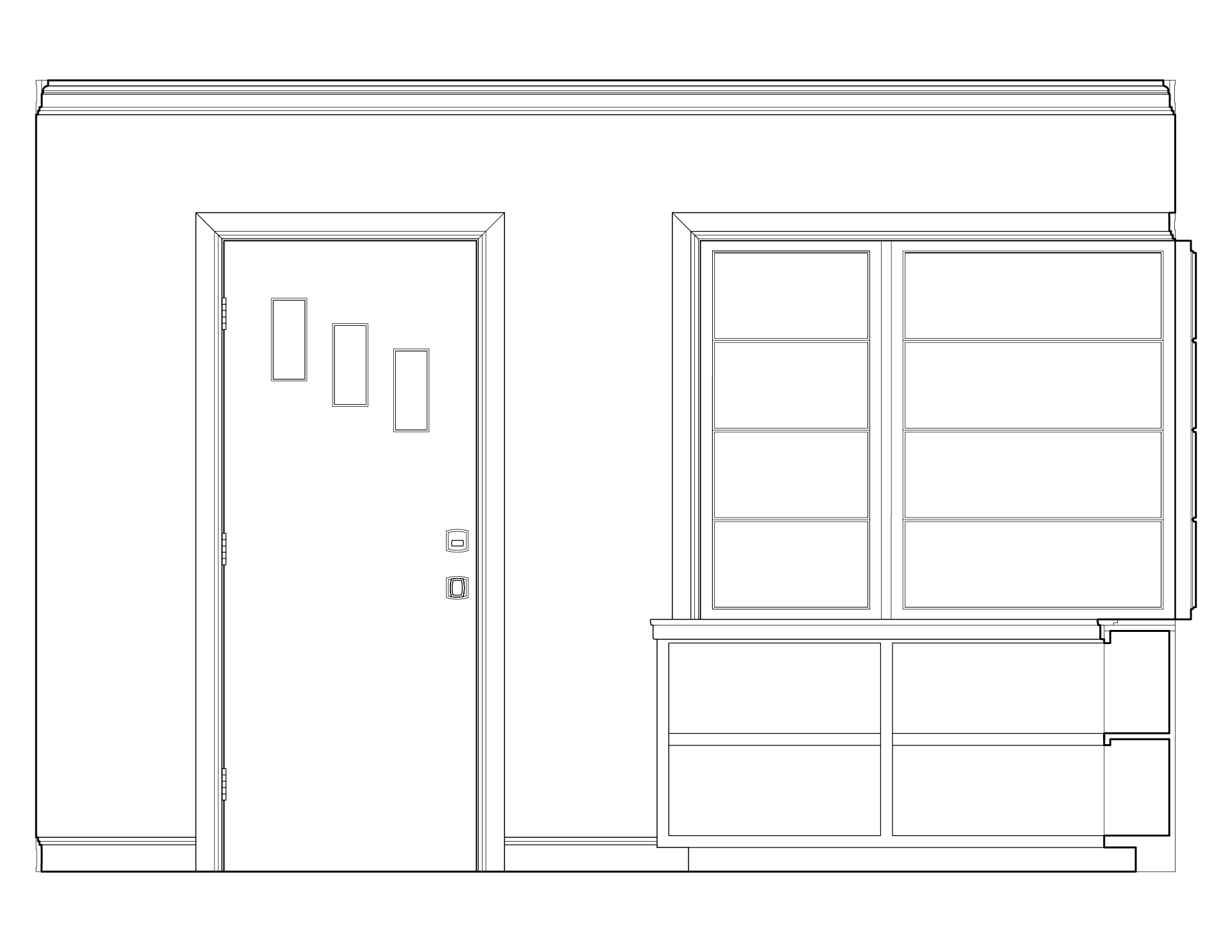
Art Moderne architecture, sometimes referred to as Streamlined Moderne, was a design style that emerged during the 1930s. The architectural style emphasized curving forms, long horizontal lines, rounded corners, flat roofs, horizontal bands of windows, and smooth walls with no ornamentation.
See examples of Art Moderne architecture & mouldings.
CHARACTERISTICS OF ART MODERNE ARCHITECTURE
The Art Moderne style developed out of Art Deco, but it has distinguishable features such as low, horizontal shapes. Art Moderne style also places an emphasis on curving forms, while triangles, zigzags, and chevrons are more commonly seen in Art Deco.
Curved window glass wrapping around corners, stainless steel window and door trim, and sunshade roofs over southern windows were also popular Art Moderne details.
Common elements of Art Moderne style:
- Emphasis on curving forms
- Simple geometric shapes
- Long horizontal lines
- Contemporary styles
- Flat roofs
- One-story buildings
- Predominately white
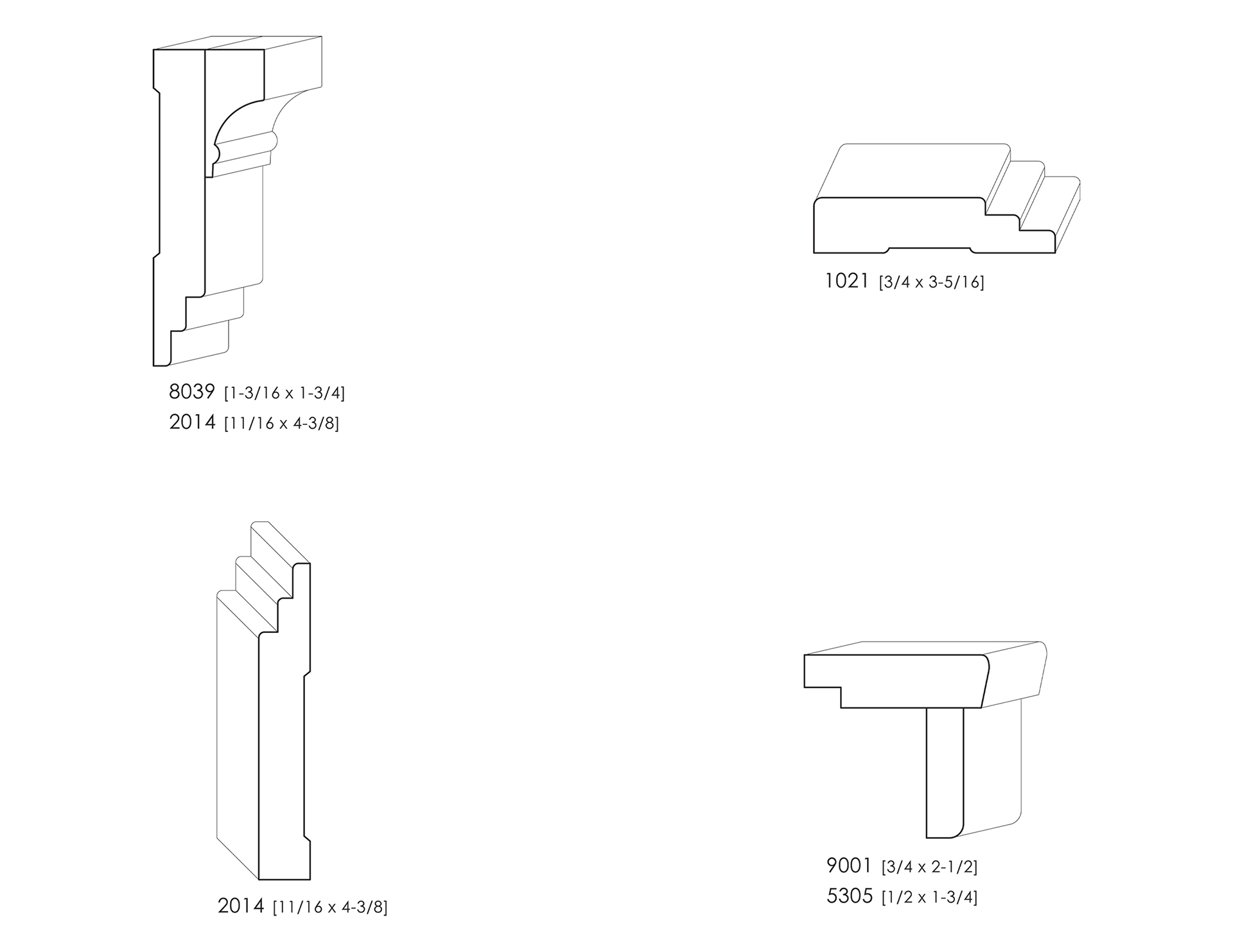
ART MODERNE STYLE MOULDINGS
Art Moderne style mouldings use long, smooth, parallel lines with soft corners and suggest the speed of the machine age.
HISTORY OF ART MODERNE ARCHITECTURE
Art Moderne style architecture was seen as a response to the Great Depression. As the world became more disciplined after the “Roaring Twenties,” industrial designers were favored over more stylistic architects. Buildings were designed to be more streamlined, as opposed to the luxurious style of Art Deco.